Supply Chain Sustainability Guidelines
United Nations Principles for Responsible Investment (UNPRI) releases supply chain sustainability guidelines aimed at helping investors assess and manage the supply chain sustainability risks of investees.
The United Nations Principles for Responsible Investment believes that general partners and limited partners can apply this guideline to supply chain due diligence and ongoing management processes.
Related Post: Microsoft Releases Supply Chain Decarbonization Report for Listed Companies
Background of Supply Chain Sustainability Guidelines
The OECD Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises on Responsible Business Conduct and the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights are the core of sustainable regulation of global supply chains. Some regional regulatory policies, such as the EU Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD), also require companies to proactively conduct due diligence on their supply chains.
For enterprises, supply chain sustainability can reduce the financial and operational risks they face, such as avoiding fines and reducing revenue losses caused by supply chain disruptions. For investors, managing the supply chain risk exposure of investees is an important means of reducing risk and is beneficial for the long-term growth of investment portfolios. Therefore, investors should consider establishing a sustainable due diligence method for the supply chain.
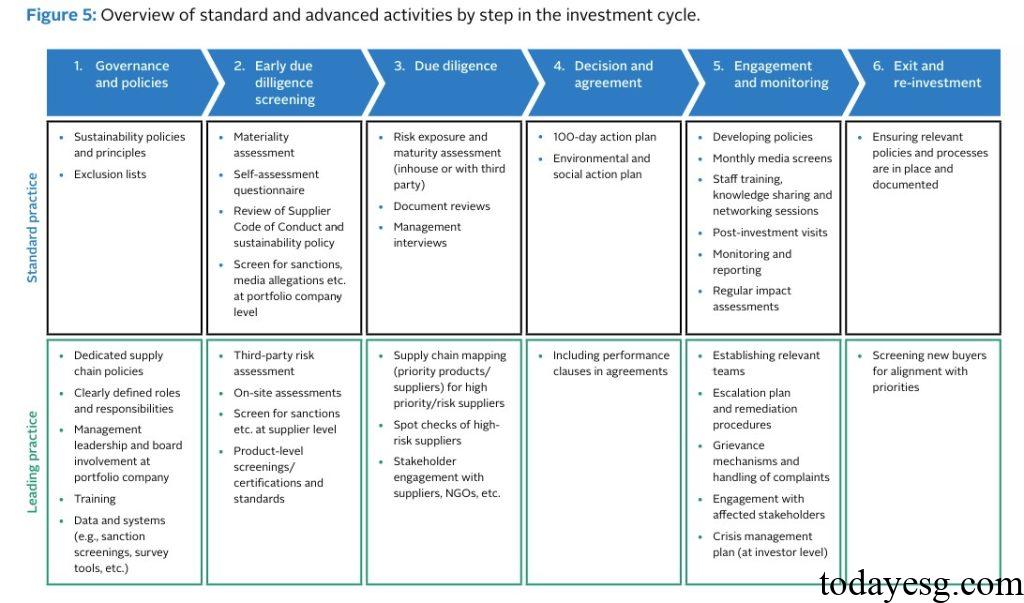
Contents of Supply Chain Sustainability Guidelines
The United Nations Principles for Responsible Investment provides investors with guidance on sustainable due diligence for supply chains, which includes:
- Governance and policies: Incorporate supply chain factors into sustainable development policies and principles and develop exclusion lists. Investors can establish specialized supply chain policies, data, and systems, clearly define roles and responsibilities, and participate in the sustainable governance process of the investees.
- Early due diligence screening: Review potential investments as early as possible to identify risks or events that may conflict with investors’ sustainable governance and policies. Investors can use materiality evaluations and other methods to raise a series of sustainability issues and review code of conduct documents to gain a preliminary understanding of supply chain sustainability risks to the investees.
- Due diligence: Conduct due diligence to identify and evaluate the impact of the supply chain, and take preventive, mitigating, or remedial measures. After preliminary screening of potential investments, investors need to assess sustainable supply chain risks, and the scope of due diligence is related to risk categories, company industries, regulatory requirements, etc.
- Decision and agreement: Ensure that investment decisions are based on due diligence results and clearly define the sustainable expectations, responsibilities, actions, and other terms of the supply chain. Investors can develop environmental and social action plans to help enterprises reduce risks and establish effective management systems. Investors can also include performance clauses in the agreement.
- Engagement and monitoring: Actively collaborate with investees to enhance supply chain due diligence capabilities and continuously improve. Investors can communicate regularly with the company, support the company in fulfilling its sustainable responsibilities, provide knowledge and technical guidance, and regularly monitor implementation.
- Exit and re-investment: Consider sustainable impacts when exiting investments. Investors can provide comprehensive sustainable data to help market participants assess the company’s sustainable development situation. Investors can also screen buyers who are suitable for the long-term development of the enterprise, ensuring that sustainable supply chain commitments will continue.
Reference:
Sustainability in Supply Chains: A Guide for Private Markets Investors





