ISO 17298 Biodiversity Standard
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) releases the world’s first biodiversity standard, aimed at providing guidance for organizations to assess the impacts, dependencies, risks, and opportunities of biodiversity.
The ISO 17298 Biodiversity Standard was developed by the Biodiversity Expert Committee and is the world’s first international standard to guide organizations in incorporating biodiversity into core strategies, operations, and decision-making processes.
Related Post: Global Reporting Initiative Releases New Version of Biodiversity Disclosure Standard
Introduction to ISO 17298 Biodiversity Standard
The International Organization for Standardization believes that over half of the global GDP ($44 trillion) is moderately or highly dependent on nature, and biodiversity risks pose regulatory, reputation, and operational risks to the organization. Biodiversity action is urgent, but there is a global lack of a common standard to help organizations take measurable and responsible actions to restore and protect biodiversity.
The biodiversity standard aims to collaborate with ISO 14001 Environmental Management Systems standards, ISO 26000 Social Responsibility standards, and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs), and have a positive impact on the Global Biodiversity Framework. The new standards apply to organizations of all sizes, regions, and industries, ensuring that biodiversity is incorporated into core governance and risk management practices, in line with global expectations for biodiversity.
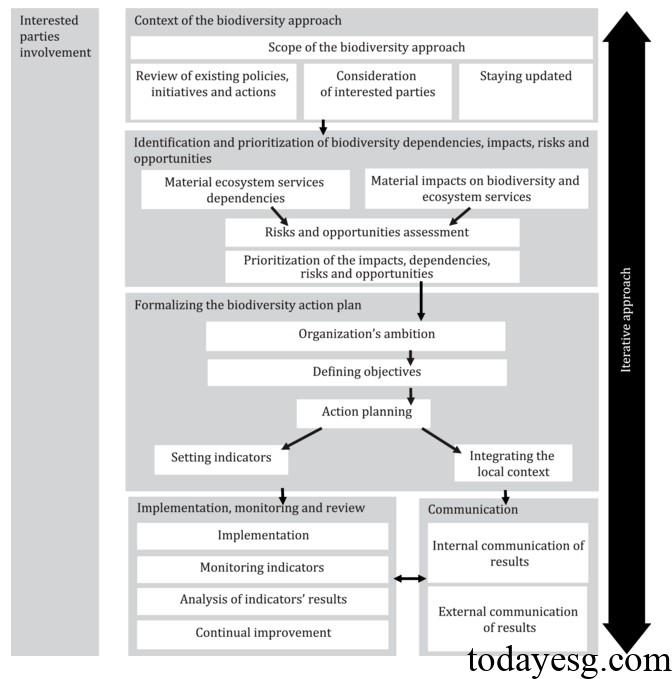
The framework of biodiversity standards is as follows:
- Scope, references, terms and definitions: Introduce the applicable objects, references, and terminology in the standard.
- Context of the biodiversity approach and involvement of interested parties: Introduce biodiversity development, existing policies, and stakeholders.
- Identifying and prioritizing biodiversity impacts, dependencies, risks and opportunities: Consider the material impacts and dependencies of the organization on biodiversity and ecosystems, conduct risk and opportunity assessments, and identify priorities.
- Formalizing the biodiversity action plan: Based on organizational planning, set goals and design action plans according to those goals.
- Communication: Communicate with internal and external stakeholders.
- Implementation, monitoring, and review: Implement the biodiversity action plan, monitor and analyze relevant indicators, and continuously improve effectiveness.
In addition to the ISO 17298 biodiversity standard, the standards still being developed by the Biodiversity Expert Committee include:
- ISO 13208 Biodiversity Vocabulary.
- ISO 17317 Requirements and guidelines for the characterization of products based on native species.
- ISO 17620 Process for designing and implementing biodiversity net gain in development projects.
- ISO 18244 Biodiversity and the Food Sector: Guidelines on how to improve biodiversity performance of food companies and food retailers.
- ISO 25182 Ecological networks mapping of standardization needs.
Reference:
ISO 17298: Biodiversity for Organizations – Guidelines and Requirements





