Carbon Credit Buyer’s Guide
The Hong Kong Exchange (HKEX) releases a carbon credit buyer’s guide, aimed at introducing the concept and mechanism of carbon credit, and helping for companies to purchase carbon credit.
The Hong Kong Exchange launched Core Climate in 2022, providing a platform for companies to purchase, settle, hold, and write off carbon credits. Currently, the platform has over 100 participants and involves more than 60 international high-quality carbon credit projects.
Related Post: HKEX Releases Carbon Market Report
Introduction to Carbon Credit
Carbon credit is a tradable unit that represents one ton of carbon dioxide avoided from being emitted or removed from the atmosphere. The cycle of carbon credits is as follows:
- Project Development: Design, implement, and manage carbon credit projects that vary in scope and type, but typically adhere to key fundamental principles such as additionality and permanence.
- Validation and Verification: The project needs to undergo review before generating carbon credits. Validation refers to the project meeting the requirements of carbon credit standards and can be submitted for registration. Confirmation refers to the quantification of project outcomes based on carbon credit standards, which is also the costliest stage in the carbon credit cycle.
- Issuance: Carbon credits are issued and tracked in the registry, and initiators can sell carbon credits to earn profits.
- Retirement: When a carbon credit buyer applies for carbon reduction, the carbon credit will be cancelled. These carbon credits will exit the market, no longer be sold or continue to circulate.
The participants in the carbon credit cycle are as follows:
- Validation and verification bodies: Third-party auditing agencies that provide validation and verification services for carbon projects.
- Standards bodies: Provide rules that must be followed when issuing carbon credits for carbon emission projects under specific standards.
- Registries: Identify, record, and track issued carbon credits.
- Marketplaces: Connect market participants to ensure real-time, secure, and traceable carbon credit trading.
- Intermediaries: Provide services to connect buyers and sellers and promote carbon credit trading.
- Rating agencies: Evaluate the quality of carbon credits and provide ratings.
- End users: Purchase and cancel carbon credits.
Nomination and Screening of Carbon Credit Projects
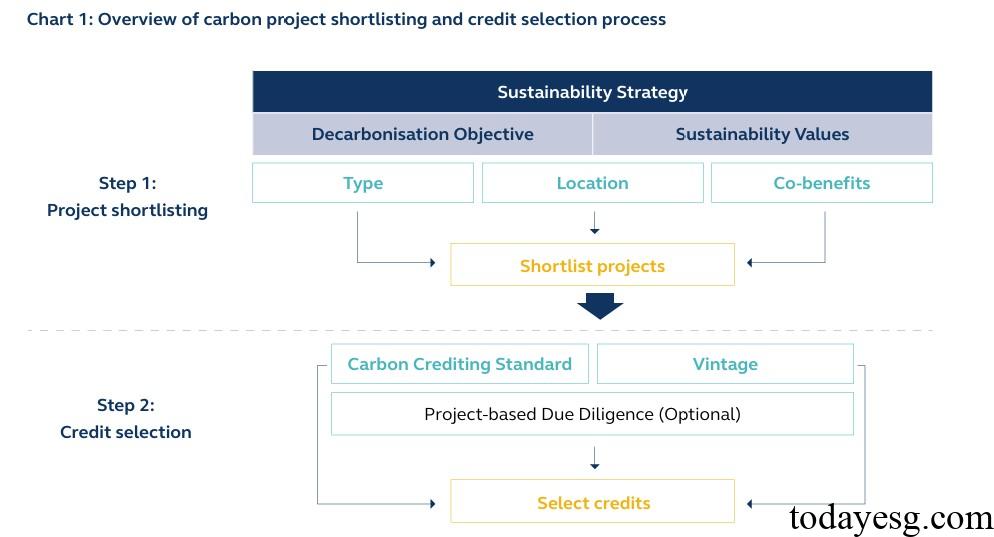
The Hong Kong Exchange provides a method for carbon credit buyers to shortlist and screen carbon credit projects, which is based on corporate sustainable development strategies and can be divided into two stages:
Phase 1: Project shortlisting, where companies can consider the following factors:
- Project type: There are two types of carbon emission projects: projects that avoid emissions and projects that eliminate emissions, and projects based on nature or technology. Avoiding emissions aims to prevent future carbon emissions, while eliminating emissions aims to eliminate current carbon dioxide. Enterprises can consider both types of projects simultaneously, but to achieve net zero, it is more important to consider projects that eliminate emissions. Nature based projects typically bring additional environmental benefits, such as increasing biodiversity and protecting ecosystems. Technology based projects typically rely on technology to avoid or eliminate emissions, such as carbon capture, utilization, and storage technologies.
- Project location: Enterprises can consider the relevance of carbon credit project locations to their operations or supply chains, as well as the project’s support for climate vulnerable areas.
- Common benefits: Synergistic benefits of carbon credit projects can help companies achieve their sustainable development strategies, and projects that provide additional environmental or social benefits may receive additional certifications.
Phase 2: Credit selection, where companies can consider the following factors:
- Carbon credit standards: Carbon credit projects need to pass standard certification, and different standards have their own scope and rules. These standards are usually divided into categories such as government management and international management.
- Carbon credit year: Carbon credit year refers to the year in which carbon emissions are avoided or cleared. The Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi) recommends selecting years from 2021 onwards to comply with the Paris Agreement. The market usually tends to favor new seasons because the standards for these carbon projects may be higher.
Reference:
HKEX Hosts Climate Finance Forum, Shaping Future Landscape of Environmental Markets





