Report on Nature-related Financial Risks
The Financial Stability Board (FSB) releases a report on nature-related financial risks, aimed at summarizing the actions of regulators in identifying and assessing nature-related financial risks.
The Financial Stability Board believes that regulators need to recognize the close connection between nature and climate, and consider the financial risks caused by both. Previously, the Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS) released a nature-related financial risk framework, providing risk measurement standards for central banks.
Related Post: NGFS Releases Framework for Nature-related Financial Risks for Central Banks
Introduction to Nature-related Financial Risks
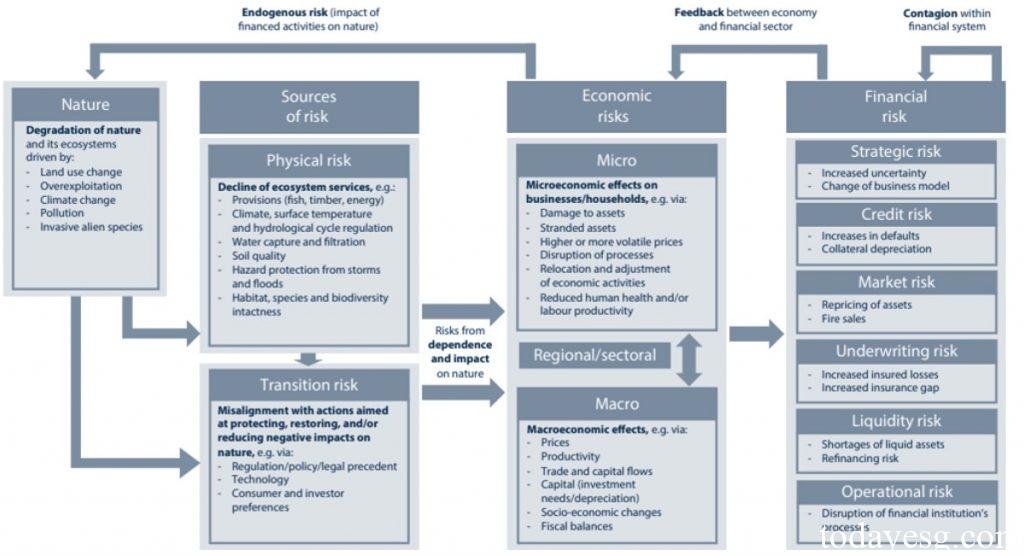
At present, there is no unified definition of nature-related financial risks globally, but many regulators are adopting the concepts proposed by the Green Finance Network. The Green Finance Network believes that nature-related financial risks refer to risks that have negative impacts on the economy, financial system, or financial institutions. These risks arise from the loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services caused by natural degradation, or from inconsistent actions to protect, restore, and reduce the negative impacts of nature.
Regulators typically use a classification approach for climate related financial risks to deal with nature-related financial risks, which are divided into physical risks and transition risks. Physical risks refer to the risks arising from the interruption of activities that directly or indirectly rely on ecosystem services due to biodiversity loss. These physical risks can be further divided into acute hazards and chronic hazards. Transition risk refers to the risks arising from actions taken to protect, restore, and reduce the negative impacts of nature. The economic costs of these risks may affect various economic entities and lead to financial risks.
Nature-related financial risks may manifest through typical financial risk channels, including:
- Credit risk: The loss of biodiversity may lead to higher credit risk for borrowers, which is common in industries such as real estate and agriculture.
- Market risk: The risk that the market value of an asset is affected by the loss of biodiversity or policy changes, which is reflected in changes in the prices of stocks and bonds held by financial institutions.
- Underwriting risk: The policyholder’s claims increase after a natural disaster, resulting in an increase in insurance costs.
The consideration of nature-related financial risks in various jurisdictions around the world is at different stages. Some regulators believe that nature-related financial risks need to be included in the regulatory scope, while others are still in the continuous monitoring stage. Some regulators have decided to prioritize climate related financial risks or temporarily not study this topic. However, some regulators believe that risks may have a transmission effect, causing a series of jurisdictions to be affected by the same event.
Identify, Assess, and Manage Nature-related Financial Risks
Regulators are taking action to identify, assess, and manage nature-related financial risks, with common actions including:
- General guidance and requirements: Regulators provide nature-related financial risk regulatory guidelines for financial institutions, covering banks, insurance companies, asset management companies, etc. For example, the European Central Bank has included nature-related financial risks in its Capital Requirements Directive and Solvency II Directive, which apply to banks and insurance companies respectively.
- Guidance and requirements on firm level disclosures: Regulators are adopting the recommendations of the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures to disclose information. For example, the European Sustainability Reporting Standards require companies to disclose information about water resources, marine resources, and biodiversity.
- Data collection: Regulators collect qualitative and quantitative data to understand the risk exposure of financial institutions and measure nature-related financial risks. For example, the European Central Bank plans to collect and evaluate ESG risk pillar data for regulated entities.
- Incorporate nature-related financial risks into a broader financial framework: Nature-related financial risks will be included in the prudential regulatory framework, just like climate related financial risks.
- Scenario analysis: Regulators can combine input-output models with biological models to effectively assess nature-related financial risks. For example, the European Central Bank used scenario analysis to evaluate the sensitivity of bank credit portfolios to changes in biodiversity.
- Capacity building: Regulators organize stakeholders to participate in meetings and jointly explore financial risks. For example, the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission (CBIRC) organizes seminars on green financial services to promote information exchange among banks.
Reference:
Supervisory and Regulatory Approaches and Perspectives on Financial Risk





