Circular Economy Financing Report
The United Nations Environment Program Finance Initiative (UNEPFI) releases a report on circular economy financing, aiming to propose a method to unleash the potential of circular economy financing.
This report is jointly written by the United Nations Environment Program Financial Initiative, the Global Alliance on Circular Economy and Resource Efficiency (GACERE), and numerous stakeholders, and provides action guidelines for regulatory agencies, financial institutions, and others.
Related Post: Introduction to the Definition, Classification, and Principles of Circular Economy
Circular Economy Financing Development
Since 2019, the global scale of circular economy financing has reached 350 billion US dollars, but it only accounts for a small portion of sustainable finance. The value of global sustainable investment products has exceeded $7 trillion by 2023. Since 1999, a total of 75 circular economy roadmaps and strategies have been released globally, of which 71 were released after 2016, but only a few have been truly implemented. At the same time, the global resource mining output continues to grow, and will increase by 60% at the current level in 2060.
Circular economy can improve resource efficiency, reduce raw material costs, enhance supply chain resilience, and establish sustainable and competitive business models. To fully unleash the potential, countries need to recognize the importance of natural resource risks, promote stakeholder cooperation, expand the scale of circular economy financing, and deploy circular economy solutions.
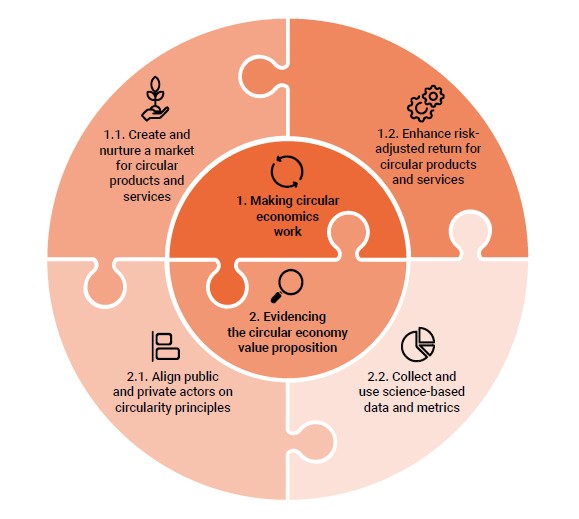
Circular Economy Financing Advice
The United Nations Environment Program Financial Initiative proposes circular economy financing advice from two aspects:
Making circular economy work: A circular economy must have financial feasibility to attract capital, which requires establishing effective markets for circular products and services and increasing risk return rates. Circular economy has long-term financial benefits, but it incurs high upfront investment costs for investors. The public sector needs to use multiple financial instruments to provide initial support to share risks. The actions of various stakeholders include:
- Government: Develop fiscal measures for circular economy, fully utilize public procurement policies, and provide financial support.
- Public financial institutions: Provide technical assistance and financial incentives, create and cultivate circular economy markets, and improve risk return ratios.
- Private financial institutions: Design and provide innovative financing tools, encourage customers to participate in circular economic business, and incorporate circular economy principles into financial decision-making.
Proving the circular economy value proposition: Current market still lacks sufficient data and evidence to support large-scale circular economic investments. Stakeholders need to reach a consensus on the principles of circular economy and help investors incorporate them into investment decisions and financing standards. Collecting and utilizing scientific data on circular economy can evaluate the adoption of policies and business practices, measure their impact on the economy, environment, and society from a full cycle perspective, and demonstrate the value of circular economy. The actions of various stakeholders include:
- Government: Develop circular economy principles, fund related research, and encourage data collection.
- Regulators: Encourage financial institutions to adopt circular economic principles and strengthen the consideration of natural risks in existing environmental assessments.
- Public financial institutions: participate in the formulation of circular economy principles, carry out circular economy pilot projects, and collect experience.
- Private financial institutions: participate in the development of circular economy principles and incorporate circular economy factors into risk return analysis.
Reference:





